When you work with Git and GitHub you can interact with HTTPS or SSH. We will provide a tutorial on how you can deploy an SSH key to your GitHub repository
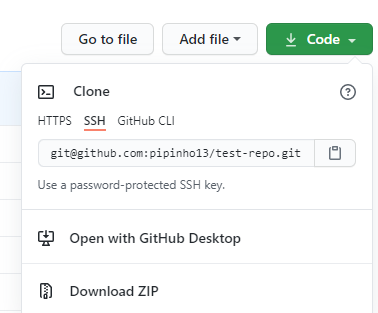
Setup an SSH Key
You can generate an SSH Key by running the ssh-keygen procedure on your computer. You will need to remember where you have saved the generated public and private rsa key pair. The steps for generating a new SSH key are:
A) Open the Git Bash
B) Copy-Paste the following command by entering your GitHub email address:
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "[email protected]"
Note: If you are using a legacy system that doesn’t support the Ed25519 algorithm, use:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
This creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label.
> Generating public/private ed25519 key pair.C) Accept the default file location when you are prompted to “Enter a file in which to save the key“
> Enter a file in which to save the key (/c/Users/you/.ssh/id_ed25519):[Press enter]D) Then you will be asked to enter a passphrase. You can leave it empty. You may have a look at passphrases.
> Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase]
> Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]Checking for existing SSH Keys
Before you generate an SSH key, you should check if you have already an existing SSH key. You can easily check for existing SSH keys using the Git Bash and entering the following command that lists the files in the .ssh directory.
ls -al ~/.ssh
By default, the filenames of the public keys are one of the following:
id_rsa.pub
id_ecdsa.pub
id_ed25519.pub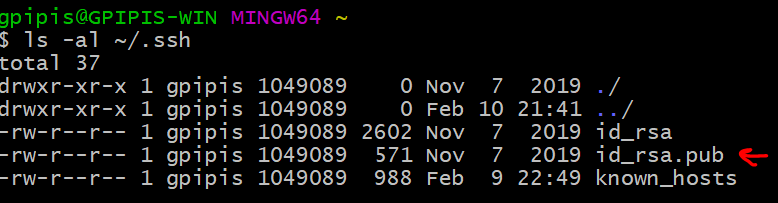
As you can see, I have an id_rsa.pub file.
Adding your SSH key to the ssh-agent
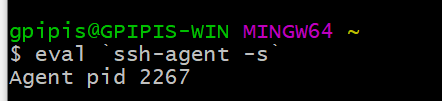
You can start the ssh-agent in the background by typing:
$ eval `ssh-agent -s`
And then you can add your private key file that you have generated by typing:
$ ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Adding the SSH key to your GitHub
You have to copy the SSH public key. There are two options. One option is to use the cat command and copy it from the terminal such as:
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub

The other option is to copy it to your clipboard by typing:
$ clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Then, go to your repository that you want to work and go the settings.
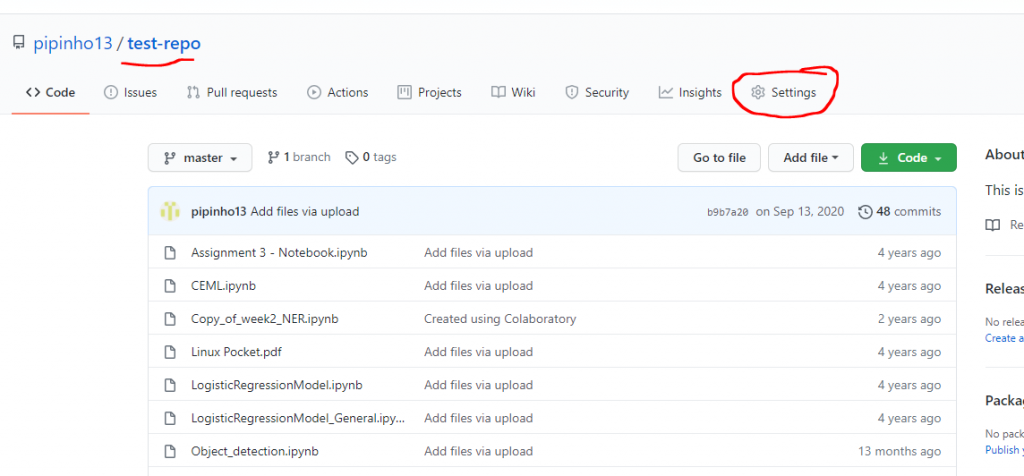
Then go the the Deploy keys:

Then Add deploy key
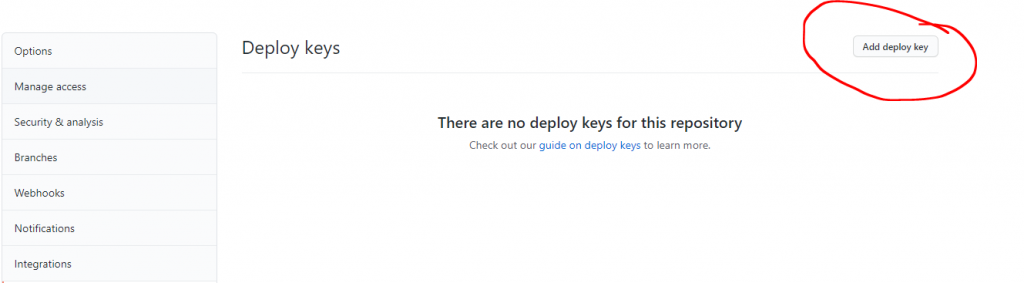
in the title section you can write whatever you want and in the key section, paste your public key and tick the Allow write access and finally click Add key and you are set!

Using Multiple Repositories
If you use multiple repositories on one server, you will need to generate a dedicated key pair for each one. You can’t reuse a deploy key for multiple repositories.
In the server’s SSH configuration file (usually ~/.ssh/config), add an alias entry for each repository. For example:
Host github.com-repo-0
Hostname github.com
IdentityFile=/home/user/.ssh/repo-0_deploy_key
Host github.com-repo-1
Hostname github.com
IdentityFile=/home/user/.ssh/repo-1_deploy_keyHost github.com-repo-0– The repository’s alias.Hostname github.com– Configures the hostname to use with the alias.IdentityFile=/home/user/.ssh/repo-0_deploy_key– Assigns a private key to the alias.
You can then use the hostname’s alias to interact with the repository using SSH, which will use the unique deploy key assigned to that alias. For example:
$ git clone [email protected]:OWNER/repo-1.git
In case that you do not have a config file, you can generate a new one as explained here. Also this post may be helpful



1 thought on “How to add an SSH Key to GitHub”
Yeah ssh doesn’t know about AD users, so you have to use a local user.