We will provide some examples of how we can reshape Pandas data frames based on our needs. We want to provide a concrete and reproducible example and for that reason, we assume that we are dealing with the following scenario.
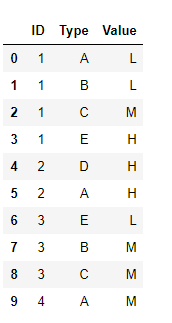
We have a data frame of three columns such as:
- ID: The UserID
- Type: The type of product.
- Value: The value of the product, like ‘H’ for High, ‘M’ for Medium and ‘L’ for Low
The data are in a long format, where each case is one row. Let’s create the data frame:
Create the Pandas Data Frame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'ID':[1,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,3,4],
'Type':['A','B','C','E','D','A','E','B','C','A'],
'Value':['L','L','M','H','H','H','L','M','M','M']})
df

Aggregate the Data by ID
Let’s say that we want to aggregate the data by ID by concatenating the text variables Type and Value respectively. We will use the lambda function and the join where our separator will be the | but it can be whatever you want.
# Aggregate the data by ID
df_agg = df.groupby('ID', as_index=False)[['Type','Value']].agg(lambda x: '|'.join(x))
df_agg
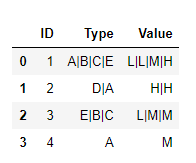
As we can see now we have 4 rows, one per each ID.
Reshape to a Long Format
Our goal is to convert the “df_agg” to the initial one. We will need some steps to achieve this.
Convert the Columns to Lists
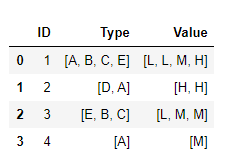
We will need to split the Type and Value columns and to transform them into lists.
df_agg['Type'] = df_agg['Type'].apply(lambda x: x.split("|"))
df_agg['Value'] = df_agg['Value'].apply(lambda x: x.split("|"))
df_agg
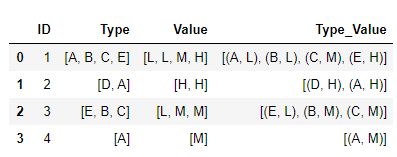
Create a list of tuples from the two column lists
We know that the elements of each list appear in order. So, we need to do a mapping between the Type and the Value list element-wise. For that reason, we will use the zip function.
df_agg['Type_Value']= df_agg.apply(lambda x: list(zip(x.Type,x.Value)), axis=1) df_agg
Exlpode the list of tuples
Now, we will explode the Type_Value as follows:
df_agg = df_agg.explode('Type_Value')
df_agg
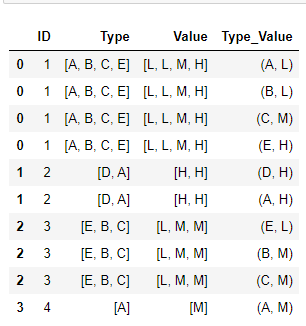
Split the tuple into two different columns
Now we want to split the tuple into two different columns, where the first one is referred to the Type and the second one to the Value.
df_agg[['New_Type','New_Value']] = pd.DataFrame(df_agg['Type_Value'].tolist(), index=df_agg.index) df_agg

Now we will keep only the columns that we want and we will rename them.
df_agg = df_agg[['ID','New_Type', 'New_Value']].\
rename(columns={"New_Type": "Type", "New_Value": "Value"}).\
reset_index(drop=True)
df_agg
Check if the Data Frames are identical
As we can see we started with a long format, we reshaped the data, and then we converted it back to the initial format. Let’s verify if the initial data frame is the same as the last one that we created.
df_agg.equals(df)
and we get True!