In this tutorial, we will provide an example of how we can train an NLP classification problem with BERT and SageMaker. ou will train a text classifier using a variant of BERT called RoBERTa within a PyTorch model ran as a SageMaker Training Job. The steps of our analysis are:
- Configure dataset
- Configure model hyper-parameters
- Setup evaluation metrics, debugger and profiler
- Train model
- Analyze debugger results
- Deploy and test the model
We will use the “Bring Your Own Script” schema.
Prepare the SageMaker Environment
import boto3
import sagemaker
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import botocore
config = botocore.config.Config(user_agent_extra='dlai-pds/c2/w2')
# low-level service client of the boto3 session
sm = boto3.client(service_name='sagemaker',
config=config)
sm_runtime = boto3.client('sagemaker-runtime',
config=config)
sess = sagemaker.Session(sagemaker_client=sm,
sagemaker_runtime_client=sm_runtime)
bucket = sess.default_bucket()
role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()
region = sess.boto_region_name
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format='retina'
Configure the Dataset
Assume that you have already split your data into train, validation and test datasets. Then we can upload this data to S3.
processed_train_data_s3_uri = 's3://{}/data/sentiment-train/'.format(bucket)
processed_validation_data_s3_uri = 's3://{}/data/sentiment-validation/'.format(bucket)
!aws s3 cp --recursive ./data/sentiment-train $processed_train_data_s3_uri
!aws s3 cp --recursive ./data/sentiment-validation $processed_validation_data_s3_uri
Then, we need to setup the input channels.
s3_input_train_data = sagemaker.inputs.TrainingInput(
s3_data=processed_train_data_s3_uri
)
s3_input_validation_data = sagemaker.inputs.TrainingInput(
s3_data=processed_validation_data_s3_uri
)
data_channels = {
'train': s3_input_train_data,
'validation': s3_input_validation_data
}
The next step is to configure the model hyper-parameters.
max_seq_length=128 # maximum number of input tokens passed to BERT model freeze_bert_layer=False # specifies the depth of training within the network epochs=3 learning_rate=2e-5 train_batch_size=256 train_steps_per_epoch=50 validation_batch_size=256 validation_steps_per_epoch=50 seed=42 run_validation=True train_instance_count=1 train_instance_type='ml.c5.9xlarge' train_volume_size=256 input_mode='File'
Some of them will be passed into the PyTorch estimator in the hyperparameters argument. Let’s setup the dictionary for that:
hyperparameters={
'max_seq_length': max_seq_length,
'freeze_bert_layer': freeze_bert_layer,
'epochs': epochs,
'learning_rate': learning_rate,
'train_batch_size': train_batch_size,
'train_steps_per_epoch': train_steps_per_epoch,
'validation_batch_size': validation_batch_size,
'validation_steps_per_epoch': validation_steps_per_epoch,
'seed': seed,
'run_validation': run_validation
}
The next step is to setup the evaluation metrics that will be the loss and the accuracy. Regex will capture the values of metrics that the algorithm will emit.
metric_definitions = [
{'Name': 'validation:loss', 'Regex': 'val_loss: ([0-9.]+)'},
{'Name': 'validation:accuracy', 'Regex': 'val_acc: ([0-9.]+)'},
]
Then we have to setup a debugger and profiler
from sagemaker.debugger import Rule, ProfilerRule, rule_configs from sagemaker.debugger import DebuggerHookConfig from sagemaker.debugger import ProfilerConfig, FrameworkProfile
DebuggerHookConfig provides options to customize how debugging information is emitted and saved. s3_output_path argument value defines the location in Amazon S3 to store the output.
debugger_hook_config = DebuggerHookConfig(
s3_output_path='s3://{}'.format(bucket),
)
ProfilerConfig sets the configuration for collecting system and framework metrics of SageMaker Training Jobs. Parameter system_monitor_interval_millis sets the time interval to collect system metrics (in milliseconds). Parameter framework_profile_params is the object for framework metrics profiling. Here you will set its local path, the step at which to start profiling, start_step, and the number of steps to profile, num_steps.
from sagemaker.debugger import ProfilerConfig, FrameworkProfile
profiler_config = ProfilerConfig(
system_monitor_interval_millis=500,
framework_profile_params=FrameworkProfile(local_path="/opt/ml/output/profiler/", start_step=5, num_steps=10)
)
For monitoring and profiling the built-in rules you can use the ProfilerReport. It creates a profiling report and updates when the individual rules are triggered. If you trigger this ProfilerReport rule without any customized parameter as in the cell below, then the ProfilerReport rule triggers all of the built-in rules for monitoring and profiling with their default parameter values.
The profiling report can be downloaded while the Training Job is running or after the job has finished.
rules=[ProfilerRule.sagemaker(rule_configs.ProfilerReport())]
Train the Model
We will use the PyTorch model running it as a SageMaker Training Job in a separate Python file, which will be called during the training, using a pre-trained model called robeta-base.
The train.py script is the following:
################################################################################################################################################
######################################################## Import required modules ###############################################################
################################################################################################################################################
import argparse
import pprint
import json
import logging
import os
import sys
import pandas as pd
import random
import time
import glob
import numpy as np
from collections import defaultdict
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data
import torch.utils.data.distributed
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from transformers import RobertaModel, RobertaConfig
from transformers import RobertaForSequenceClassification
from transformers import AdamW, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
################################################################################################################################################
###################################################### Parse input arguments ###################################################################
################################################################################################################################################
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# CLI args
parser.add_argument('--train_batch_size',
type=int,
default=64)
parser.add_argument('--train_steps_per_epoch',
type=int,
default=64)
parser.add_argument('--validation_batch_size',
type=int,
default=64)
parser.add_argument('--validation_steps_per_epoch',
type=int,
default=64)
parser.add_argument('--epochs',
type=int,
default=1)
parser.add_argument('--freeze_bert_layer',
type=eval,
default=False)
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate',
type=float,
default=0.01)
parser.add_argument('--momentum',
type=float,
default=0.5)
parser.add_argument('--seed',
type=int,
default=42)
parser.add_argument('--log_interval',
type=int,
default=100)
parser.add_argument('--backend',
type=str,
default=None)
parser.add_argument('--max_seq_length',
type=int,
default=128)
parser.add_argument('--run_validation',
type=eval,
default=False)
# Container environment
parser.add_argument('--hosts',
type=list,
default=json.loads(os.environ['SM_HOSTS']))
parser.add_argument('--current_host',
type=str,
default=os.environ['SM_CURRENT_HOST'])
parser.add_argument('--model_dir',
type=str,
default=os.environ['SM_MODEL_DIR'])
parser.add_argument('--train_data',
type=str,
default=os.environ['SM_CHANNEL_TRAIN'])
parser.add_argument('--validation_data',
type=str,
default=os.environ['SM_CHANNEL_VALIDATION'])
parser.add_argument('--output_dir',
type=str,
default=os.environ['SM_OUTPUT_DIR'])
parser.add_argument('--num_gpus',
type=int,
default=os.environ['SM_NUM_GPUS'])
# Debugger args
parser.add_argument("--save-frequency",
type=int,
default=10,
help="frequency with which to save steps")
parser.add_argument("--smdebug_path",
type=str,
help="output directory to save data in",
default="/opt/ml/output/tensors",)
parser.add_argument("--hook-type",
type=str,
choices=["saveall", "module-input-output", "weights-bias-gradients"],
default="saveall",)
return parser.parse_args()
################################################################################################################################################
########################################################### Tools and variables ################################################################
################################################################################################################################################
# Model name according to the PyTorch documentation:
# https://github.com/aws/sagemaker-pytorch-inference-toolkit/blob/6936c08581e26ff3bac26824b1e4946ec68ffc85/src/sagemaker_pytorch_serving_container/torchserve.py#L45
MODEL_NAME = 'model.pth'
# Hugging face list of models: https://huggingface.co/models
PRE_TRAINED_MODEL_NAME = 'roberta-base'
def create_list_input_files(path):
input_files = glob.glob('{}/*.tsv'.format(path))
print(input_files)
return input_files
def save_transformer_model(model, model_dir):
path = '{}/transformer'.format(model_dir)
os.makedirs(path, exist_ok=True)
print('Saving Transformer model to {}'.format(path))
model.save_pretrained(path)
def save_pytorch_model(model, model_dir):
os.makedirs(model_dir, exist_ok=True)
print('Saving PyTorch model to {}'.format(model_dir))
save_path = os.path.join(model_dir, MODEL_NAME)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_path)
################################################################################################################################################
########################################################### Configure the model ################################################################
################################################################################################################################################
def configure_model():
classes = [-1, 0, 1]
config = RobertaConfig.from_pretrained(
PRE_TRAINED_MODEL_NAME,
num_labels=len(classes),
id2label={
### BEGIN SOLUTION - DO NOT delete this comment for grading purposes
0: -1, # Replace all None
1: 0, # Replace all None
2: 1, # Replace all None
### END SOLUTION - DO NOT delete this comment for grading purposes
},
label2id={
-1: 0,
0: 1,
1: 2,
}
)
config.output_attentions=True
return config
################################################################################################################################################
####################################################### PyTorch Dataset and DataLoader #########################################################
################################################################################################################################################
# PyTorch dataset retrieves the dataset’s features and labels one sample at a time
# Create a custom Dataset class for the reviews
class ReviewDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, input_ids_list, label_id_list):
self.input_ids_list = input_ids_list
self.label_id_list = label_id_list
def __len__(self):
return len(self.input_ids_list)
def __getitem__(self, item):
# convert list of token_ids into an array of PyTorch LongTensors
input_ids = json.loads(self.input_ids_list[item])
label_id = self.label_id_list[item]
input_ids_tensor = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
label_id_tensor = torch.tensor(label_id, dtype=torch.long)
return input_ids_tensor, label_id_tensor
# PyTorch DataLoader helps to to organise the input training data in “minibatches” and reshuffle the data at every epoch
# It takes Dataset as an input
def create_data_loader(path, batch_size):
print("Get data loader")
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['input_ids', 'label_id'])
input_files = create_list_input_files(path)
for file in input_files:
df_temp = pd.read_csv(file,
sep='\t',
usecols=['input_ids', 'label_id'])
df = df.append(df_temp)
ds = ReviewDataset(
input_ids_list=df.input_ids.to_numpy(),
label_id_list=df.label_id.to_numpy(),
)
return DataLoader(
ds,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True,
), df
################################################################################################################################################
################################################################ Train model ###################################################################
################################################################################################################################################
def train_model(model,
train_data_loader,
df_train,
val_data_loader,
df_val,
args):
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
if args.freeze_bert_layer:
print('Freezing BERT base layers...')
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if 'classifier' not in name: # classifier layer
param.requires_grad = False
print('Set classifier layers to `param.requires_grad=False`.')
train_correct = 0
train_total = 0
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
print('EPOCH -- {}'.format(epoch))
for i, (sent, label) in enumerate(train_data_loader):
if i < args.train_steps_per_epoch:
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
sent = sent.squeeze(0)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
sent = sent.cuda()
label = label.cuda()
output = model(sent)[0]
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
loss = loss_function(output, label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if args.run_validation and i % args.validation_steps_per_epoch == 0:
print('RUNNING VALIDATION:')
correct = 0
total = 0
model.eval()
for sent, label in val_data_loader:
sent = sent.squeeze(0)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
sent = sent.cuda()
label = label.cuda()
output = model(sent)[0]
_, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)
total += label.size(0)
correct += (predicted.cpu() ==label.cpu()).sum()
accuracy = 100.00 * correct.numpy() / total
print('[epoch/step: {0}/{1}] val_loss: {2:.2f} - val_acc: {3:.2f}%'.format(epoch, i, loss.item(), accuracy))
else:
break
print('TRAINING COMPLETED.')
return model
################################################################################################################################################
#################################################################### Main ######################################################################
################################################################################################################################################
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Parse args
args = parse_args()
print('Loaded arguments:')
print(args)
# Get environment variables
env_var = os.environ
print('Environment variables:')
pprint.pprint(dict(env_var), width = 1)
# Check if distributed training
is_distributed = len(args.hosts) > 1 and args.backend is not None
print("Distributed training - {}".format(is_distributed))
use_cuda = args.num_gpus > 0
print("Number of gpus available - {}".format(args.num_gpus))
kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
device = torch.device('cuda' if use_cuda else 'cpu')
# Initialize the distributed environment.
if is_distributed:
world_size = len(args.hosts)
os.environ['WORLD_SIZE'] = str(world_size)
host_rank = args.hosts.index(args.current_host)
os.environ['RANK'] = str(host_rank)
dist.init_process_group(backend=args.backend, rank=host_rank, world_size=world_size)
print('Initialized the distributed environment: \'{}\' backend on {} nodes. '.format(
args.backend, dist.get_world_size()) + 'Current host rank is {}. Number of gpus: {}'.format(
dist.get_rank(), args.num_gpus))
# Set the seed for generating random numbers
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
if use_cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed(args.seed)
# Instantiate model
config = None
model = None
successful_download = False
retries = 0
while (retries < 5 and not successful_download):
try:
# Configure model
config = configure_model()
model = RobertaForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
'roberta-base',
config=config
)
model.to(device)
successful_download = True
print('Sucessfully downloaded after {} retries.'.format(retries))
except:
retries = retries + 1
random_sleep = random.randint(1, 30)
print('Retry #{}. Sleeping for {} seconds'.format(retries, random_sleep))
time.sleep(random_sleep)
if not model:
print('Not properly initialized...')
# Create data loaders
train_data_loader, df_train = create_data_loader(args.train_data, args.train_batch_size)
val_data_loader, df_val = create_data_loader(args.validation_data, args.validation_batch_size)
print("Processes {}/{} ({:.0f}%) of train data".format(
len(train_data_loader.sampler), len(train_data_loader.dataset),
100. * len(train_data_loader.sampler) / len(train_data_loader.dataset)
))
print("Processes {}/{} ({:.0f}%) of validation data".format(
len(val_data_loader.sampler), len(val_data_loader.dataset),
100. * len(val_data_loader.sampler) / len(val_data_loader.dataset)
))
print('model_dir: {}'.format(args.model_dir))
print('model summary: {}'.format(model))
callbacks = []
initial_epoch_number = 0
# Start training
model = train_model(
model,
train_data_loader,
df_train,
val_data_loader,
df_val,
args
)
save_transformer_model(model, args.model_dir)
save_pytorch_model(model, args.model_dir)
# Prepare for inference which will be used in deployment
# You will need three files for it: inference.py, requirements.txt, config.json
inference_path = os.path.join(args.model_dir, "code/")
os.makedirs(inference_path, exist_ok=True)
os.system("cp inference.py {}".format(inference_path))
os.system("cp requirements.txt {}".format(inference_path))
os.system("cp config.json {}".format(inference_path))
Now, we will call the script:
import sys, importlib
sys.path.append('src/')
import train
# reload the module if it has been previously loaded
if 'train' in sys.modules:
importlib.reload(train)
# Ignore warnings below
config = train.configure_model()
label_0 = config.id2label[0]
label_1 = config.id2label[1]
label_2 = config.id2label[2]
updated_correctly = False
if label_0 != -1 or label_1 != 0 or label_2 != 1:
print('#######################################################################################')
print('Please check that the function \'configure_model\' in the file src/train.py is complete.')
print('########################################################################################')
raise Exception('Please check that the function \'configure_model\' in the file src/train.py is complete.')
else:
print('##################')
print('Updated correctly!')
print('##################')
updated_correctly = True
Then we setup the PyTorch estimator to train our model.
from sagemaker.pytorch import PyTorch as PyTorchEstimator
if updated_correctly:
estimator = PyTorchEstimator(
entry_point='train.py',
source_dir='src',
role=role,
instance_count=train_instance_count,
instance_type=train_instance_type,
volume_size=train_volume_size,
py_version='py3', # dynamically retrieves the correct training image (Python 3)
framework_version='1.6.0', # dynamically retrieves the correct training image (PyTorch)
hyperparameters=hyperparameters,
metric_definitions=metric_definitions,
input_mode=input_mode,
debugger_hook_config=debugger_hook_config,
profiler_config=profiler_config,
rules=rules
)
Then, we launch the SageMaker Training Job which will be fitting the model to the dataset.
estimator.fit(
inputs=data_channels,
wait=False
)
training_job_name = estimator.latest_training_job.name
print('Training Job name: {}'.format(training_job_name))
training_job_name = estimator.latest_training_job.describe()['TrainingJobName']
print('Training Job name: {}'.format(training_job_name))
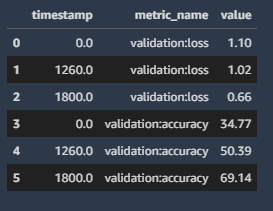
Review the training metrics
df_metrics = estimator.training_job_analytics.dataframe() df_metrics
Deploy the Model
We create a custom SentimentPredictor that encapsulates a JSONLines serializer and deserializer. To be passed into the PyTorchModel it needs to be wrapped as a class.
from sagemaker.predictor import Predictor
from sagemaker.serializers import JSONLinesSerializer
from sagemaker.deserializers import JSONLinesDeserializer
class SentimentPredictor(Predictor):
def __init__(self, endpoint_name, sagemaker_session):
super().__init__(endpoint_name,
sagemaker_session=sagemaker_session,
serializer=JSONLinesSerializer(),
deserializer=JSONLinesDeserializer())
import time
from sagemaker.pytorch.model import PyTorchModel
timestamp = int(time.time())
pytorch_model_name = '{}-{}-{}'.format(training_job_name, 'pt', timestamp)
model = PyTorchModel(name=pytorch_model_name,
model_data=estimator.model_data,
predictor_cls=SentimentPredictor,
entry_point='inference.py',
source_dir='src',
framework_version='1.6.0',
py_version='py3',
role=role)
import time
pytorch_endpoint_name = '{}-{}-{}'.format(training_job_name, 'pt', timestamp)
print(pytorch_endpoint_name)
%%time
predictor = model.deploy(initial_instance_count=1,
instance_type='ml.m5.large',
endpoint_name=pytorch_endpoint_name)
Test the Model
Here, we will pass sample strings of text to the endpoint in order to see the sentiment. We give you one example of each, however, feel free to play around and change the strings yourself!
inputs = [
{"features": ["I love this product!"]},
{"features": ["OK, but not great."]},
{"features": ["This is not the right product."]},
]
predictor = SentimentPredictor(endpoint_name=pytorch_endpoint_name,
sagemaker_session=sess)
predicted_classes = predictor.predict(inputs)
for predicted_class in predicted_classes:
print("Predicted class {} with probability {}".format(predicted_class['predicted_label'], predicted_class['probability']))
Output:
Predicted class 1 with probability 0.9605445861816406
Predicted class 0 with probability 0.5798221230506897
Predicted class -1 with probability 0.7667604684829712